FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
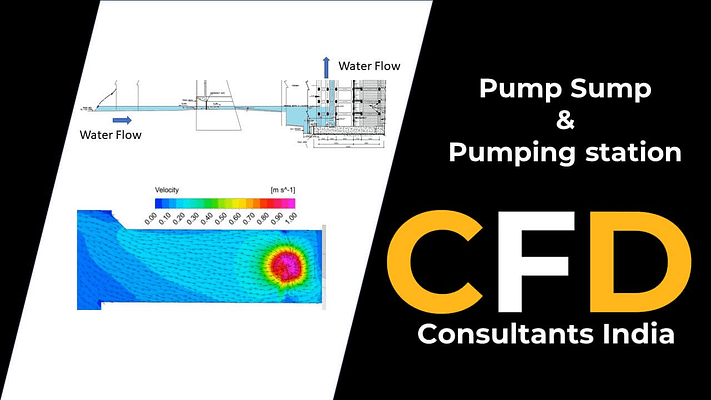
A pump sump is a structural component in pumping systems designed to collect and store fluids before they are pumped. It serves as a reservoir that ensures a continuous and uniform flow of fluid to the pump. Pump sumps play a crucial role in preventing air entrainment, vortex formation, and flow disturbances, which can affect the efficiency and reliability of pumping operations.
Pump sumps find applications in a wide range of industries, including wastewater treatment, mining, agriculture, and industrial processes. They are commonly used in situations where fluids need to be transported or drained, such as sewage pumping stations, irrigation systems, mining dewatering, and industrial cooling systems. Pump sumps are essential for maintaining the smooth and efficient operation of pumps in these applications.
Certainly. Industries such as municipal wastewater treatment plants depend on pump sumps to collect and transfer sewage. Similarly, the mining industry employs pump sumps to handle water removal from underground mines. Agriculture utilizes pump sumps for irrigation and drainage purposes. Moreover, manufacturing facilities often require pump sumps for processes involving the circulation of coolants or the transfer of fluids within their operations.
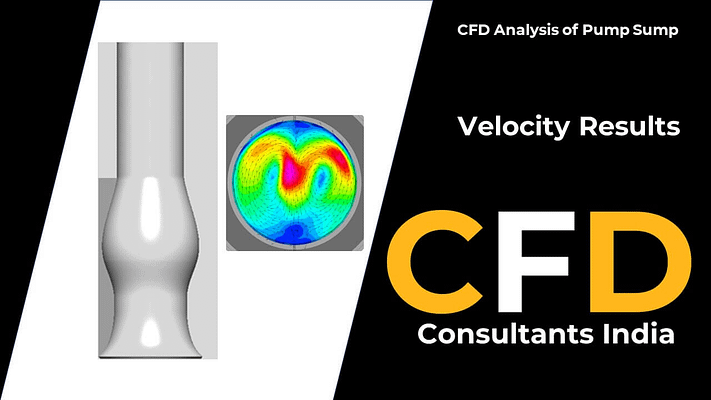
The primary objective of a CFD analysis in this context is to thoroughly assess the hydraulic behavior and flow patterns within the pump sump. It helps identify potential issues, optimize sump design, and propose modifications to enhance flow uniformity, prevent vortex formation, and improve pump efficiency.
The CFD analysis provides a detailed understanding of flow velocities, pressure distributions, and flow patterns within the sump. It identifies areas of flow disturbances, recirculation zones, and potential vortex formation. Design modifications, such as adjusting dimensions or incorporating flow control devices, can then be proposed to optimize the sump’s geometry for improved performance.